Trezor Data Breach: Lessons for Hardware Wallet Manufacturers

In today’s digital age, cybersecurity has become a paramount concern for individuals and businesses alike. With the increasing popularity of cryptocurrencies, the need to safeguard digital assets has never been more critical. However, even the most robust security measures can still prove vulnerable, as evidenced by the recent Trezor data breach.
Trezor, one of the leading hardware wallet manufacturers, fell victim to a sophisticated attack that compromised the personal information and cryptocurrency holdings of countless users. This unfortunate incident serves as a wake-up call for other hardware wallet manufacturers, highlighting the need for constant vigilance and improved security protocols.
One of the key lessons to be learned from the Trezor data breach is the importance of multifactor authentication. By implementing additional layers of security, such as biometrics or one-time passcodes, manufacturers can greatly reduce the risk of unauthorized access. These extra security measures should be seamlessly integrated into the wallet’s design to ensure a user-friendly experience without sacrificing security.
Furthermore, the Trezor data breach underscores the significance of regular security audits and updates. Hardware wallet manufacturers must stay one step ahead of cybercriminals by conducting thorough assessments of their systems and promptly addressing any vulnerabilities. This proactive approach will help prevent potential breaches and protect users’ assets.
In conclusion, the Trezor data breach serves as a powerful reminder that no security system is foolproof. As hardware wallet manufacturers strive to provide the highest level of protection for their users, the lessons learned from this incident must be heeded. By implementing robust multifactor authentication and conducting regular security audits, manufacturers can minimize the risk for users and mitigate the potential damage of future data breaches.
Trezor Data Breach: What Went Wrong
Trezor, a well-known hardware wallet manufacturer, recently experienced a data breach that left its customers vulnerable to potential attacks. This incident raised concerns among cryptocurrency enthusiasts and highlighted the importance of robust security measures in the hardware wallet industry.
Poor Security Practices

One of the key issues that led to the data breach was poor security practices on the part of Trezor. The company failed to implement proper encryption and authentication mechanisms, leaving their users’ sensitive information exposed. This oversight opened the door for malicious actors to gain unauthorized access to the data and potentially compromise the wallets.
Lack of Regular Software Updates
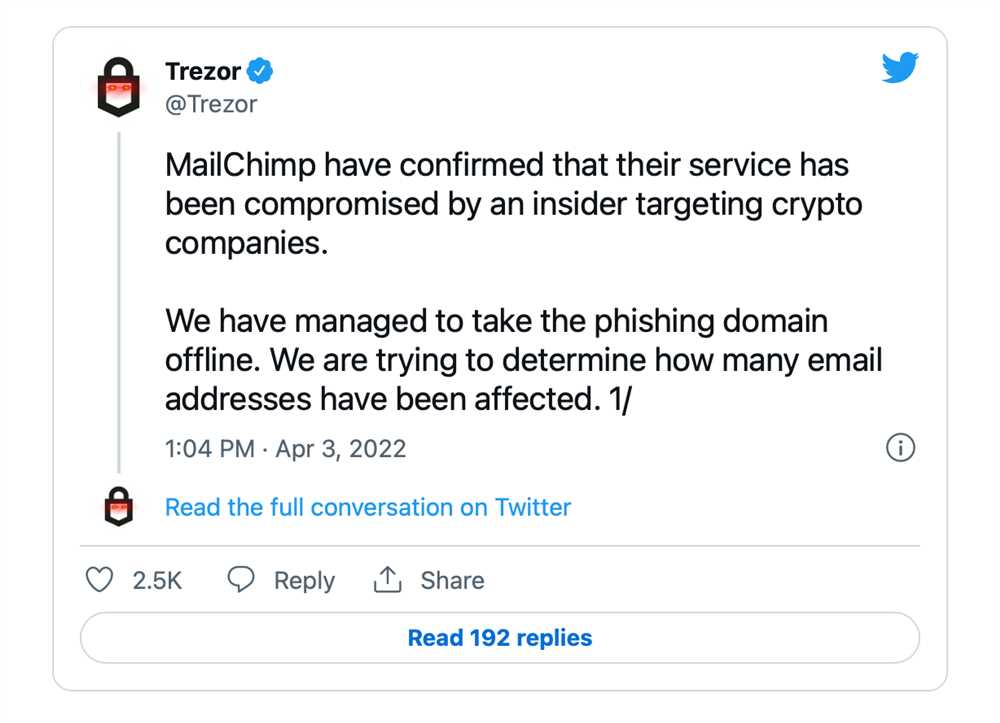
Trezor’s failure to provide regular software updates also played a significant role in the data breach. Without regular updates, vulnerabilities and weaknesses in the system were not addressed promptly, leaving the hardware wallets susceptible to exploitation. A timely patch management process could have prevented the breach or minimized its impact.
Insufficient user education
Another aspect that contributed to the breach was the lack of sufficient user education. While Trezor provided basic instructions for using their hardware wallets, they did not emphasize the importance of certain security best practices, such as setting up strong passwords and enabling two-factor authentication. This lack of guidance made it easier for attackers to exploit weak points in the users’ security practices.
Limited response plan
Trezor’s response to the data breach seemed to be lacking in several areas. The company did not have a comprehensive incident response plan in place, which delayed their ability to effectively address the breach and notify customers about potential risks. Furthermore, the communication strategy during the aftermath of the breach was subpar, causing confusion among users and further damaging the company’s reputation.
| Lessons Learned |
|---|
| 1. Implement strong encryption and authentication mechanisms to protect user data. |
| 2. Regularly update hardware wallet software to address vulnerabilities and weaknesses. |
| 3. Provide comprehensive user education on security best practices. |
| 4. Develop and test a robust incident response plan to mitigate the impact of potential breaches. |
In conclusion, the Trezor data breach serves as a cautionary tale for other hardware wallet manufacturers. By learning from the mistakes made by Trezor, the industry can take steps to enhance the security, integrity, and resilience of hardware wallets, ultimately ensuring the safety of customers’ cryptocurrency assets.
Lessons for Hardware Wallet Manufacturers
The Trezor data breach serves as a clear reminder to all hardware wallet manufacturers that security should be the utmost priority when developing and producing these devices. The breach not only compromised the personal and financial information of users but also shook the confidence of the entire cryptocurrency community.
Invest in Robust Security Measures: Hardware wallet manufacturers need to invest heavily in robust security measures to protect user data. This includes implementing strong encryption algorithms, conducting regular security audits, and adopting industry best practices to ensure the highest level of protection.
Anticipate Advanced Cybersecurity Threats: Manufacturers must stay one step ahead of hackers and anticipate advanced cybersecurity threats. This requires continuous monitoring of evolving cyber threats, collaborating with cybersecurity experts, and updating security protocols to counter new attack vectors.
Transparent Vulnerability Disclosure: Manufacturers should adopt a transparent approach to vulnerability disclosure to gain the trust of their users. Timely and public disclosure of any security vulnerabilities ensures that users are informed and allows for a swift response from the manufacturer to address the issue.
User Education and Awareness: Hardware wallet manufacturers need to prioritize user education and awareness. Many users are not aware of the potential risks and best practices when it comes to securing their cryptocurrency assets. Manufacturers should provide clear instructions on setting up and using their devices securely, as well as educate users about the importance of regularly updating firmware and being cautious of phishing attempts.
Continuous Improvement: The Trezor data breach serves as a wake-up call for all hardware wallet manufacturers to continuously improve their security measures. This includes actively seeking feedback from users, conducting regular security assessments, and implementing necessary updates to ensure the highest level of protection.
By learning from the lessons of the Trezor data breach, hardware wallet manufacturers can strengthen the security of their devices and restore the trust of the cryptocurrency community. It is crucial for the industry to prioritize security and take proactive steps to prevent future breaches.
The Impact of the Trezor Data Breach
The Trezor data breach had a significant impact on both the company and its customers. The exposure of sensitive information, such as email addresses, usernames, and encrypted passwords, raised concerns about the security of the device and the safety of cryptocurrency assets stored within it.
Customer Loss of Trust
One of the immediate impacts of the data breach was the loss of trust in Trezor as a hardware wallet manufacturer. Customers who had placed their faith in the company’s ability to safeguard their digital assets were now left questioning the reliability of the device and its security measures. This loss of trust has the potential to drive customers away from Trezor and towards alternative hardware wallet manufacturers.
Financial and Reputational Damage

In addition to the loss of customer trust, the data breach also caused financial and reputational damage to Trezor. The company had to invest time and resources into investigating the breach, identifying its cause, and implementing measures to prevent similar incidents in the future. Moreover, the negative publicity surrounding the incident put a dent in the company’s reputation, making it harder to attract new customers and retain existing ones.
| Impact | Description |
|---|---|
| Financial Loss | Trezor may have experienced financial losses due to the breach, including potential lawsuits and compensation costs. |
| Legal and Regulatory Scrutiny | The data breach may have subjected Trezor to legal and regulatory investigations, potentially leading to penalties or fines. |
| Industry-wide Consequences | The data breach served as a wakeup call for other hardware wallet manufacturers, highlighting the need for increased security measures in this industry. |
In summary, the Trezor data breach had a significant impact on the company, its customers, and the hardware wallet industry as a whole. It caused a loss of trust in Trezor, financial and reputational damage, and potential legal and regulatory consequences. It also served as a warning to other manufacturers about the importance of prioritizing security and implementing robust measures to protect customers’ sensitive information and digital assets.
Why Hardware Wallet Security is a Top Concern
When it comes to storing and protecting our cryptocurrencies, security is paramount. With the increasing popularity and value of cryptocurrencies, hackers are becoming more sophisticated in their attempts to steal these digital assets. This has made hardware wallet security a top concern for both individual users and the companies that manufacture these devices.
Hardware wallets are physical devices specifically designed to secure private keys and facilitate transactions in a safe manner. These wallets offer an extra layer of protection compared to software wallets and online exchanges, as the private keys never leave the device.
There are several reasons why hardware wallet security is a top concern:
1. Offline Private Key Storage
One of the main advantages of hardware wallets is their ability to store private keys offline. Since private keys are generated and stored within the device, they are not susceptible to online attacks or software vulnerabilities. This significantly reduces the risk of unauthorized access and unauthorized transactions.
2. Secure Transaction Signing

Hardware wallets provide a secure environment for signing transactions. When a user wants to send funds, the hardware wallet requires physical confirmation from the user to authorize the transaction. This ensures that even if the computer or mobile device used for accessing the wallet is compromised, the funds cannot be transferred without the user’s explicit consent.
Additionally, hardware wallets use multi-factor authentication methods, such as PIN codes or biometrics, to further protect against unauthorized access.
3. Protection Against Malicious Software

One of the primary risks in the cryptocurrency world is the presence of malicious software, such as keyloggers or screen capture malware. These tools can steal private keys or sensitive information and compromise the security of software wallets or online exchanges.
Hardware wallets are designed to be immune to such attacks. The devices have built-in security measures that ensure the integrity of the transactions, even in the presence of malicious software on the computer or mobile device.
Overall, hardware wallet security is a top concern due to the increasing value and popularity of cryptocurrencies, as well as the potential risks associated with online attacks and malicious software. By using a hardware wallet, users can have peace of mind knowing that their private keys are stored offline and transactions are securely signed within the device, protecting their digital assets from unauthorized access and theft.
Best Practices for Securing Hardware Wallets
The recent Trezor data breach has highlighted the importance of implementing strong security measures for hardware wallets. With the growing popularity of cryptocurrencies, it’s crucial for manufacturers to prioritize the protection of user funds. Here are some best practices for securing hardware wallets:
1. Secure Manufacturing Process

Manufacturers should implement rigorous security protocols throughout the production process to prevent any tampering or compromise. This includes ensuring the integrity of the supply chain, regularly inspecting and verifying the components used, and implementing secure manufacturing environments.
2. Multi-Factor Authentication
Hardware wallets should offer multi-factor authentication to provide an extra layer of security. This can involve requiring a combination of passwords, PINs, or biometric authentication methods like fingerprint or facial recognition.
3. Secure Firmware Updates
Regular firmware updates are essential for addressing vulnerabilities and improving security. Manufacturers should ensure that the firmware update process is secure and verified to prevent unauthorized modifications or malicious firmware being installed.
4. Robust Encryption
Hardware wallets should use robust encryption algorithms to protect sensitive data. This includes encrypting private keys, PINs, and other user information stored on the device. Additionally, the encryption should be resistant to brute force attacks.
5. Independent Code Audits
Manufacturers should regularly conduct independent code audits to identify any potential vulnerabilities or weaknesses in the wallet’s software. This helps ensure that the codebase is secure and free from any malicious or exploitable code.
6. Secure Backup and Recovery
Hardware wallets should have a secure backup and recovery process to protect against the loss or theft of the device. This can involve providing a passphrase or seed phrase that can be used to recover the wallet on a new device.
7. Physical Security Measures
Manufacturers should implement physical security measures to protect against theft, tampering, or unauthorized access to the hardware wallets. This can include tamper-evident packaging, secure storage during transit, and the use of anti-tampering mechanisms on the device itself.
By following these best practices, hardware wallet manufacturers can enhance the security of their devices and provide users with the peace of mind that their funds are safely protected.
Lessons Learned from the Trezor Data Breach
The Trezor data breach served as a wake-up call for the entire hardware wallet industry, highlighting the potential vulnerabilities and risks that exist. This incident sheds light on several key lessons that can help other hardware wallet manufacturers enhance their security measures and protect their users’ digital assets.
1. Prioritize Security Audits
One of the most important takeaways from the Trezor data breach is the critical need for regular security audits. Manufacturers should conduct thorough and independent audits of their hardware wallets, seeking the expertise of external security professionals. This will help identify any potential vulnerabilities and ensure that robust security measures are in place to prevent data breaches.
2. Implement Multi-layered Security
Trezor’s data breach was a result of a single point of failure, where an attacker gained unauthorized access to the firmware. This highlights the importance of implementing multi-layered security measures that go beyond just the firmware. Hardware wallet manufacturers should consider incorporating additional layers of security, including encryption, tamper-proof designs, and physical security features.
3. Regular Firmware Updates
Another lesson learned from the Trezor data breach is the importance of regularly updating firmware. Manufacturers should ensure that their hardware wallets are equipped with automated firmware update capabilities. This allows users to keep their devices up to date with the latest security patches and bug fixes, protecting them from potential vulnerabilities.
4. Improve User Education
Hardware wallet manufacturers should focus on improving user education and awareness about potential threats and best security practices. This includes providing clear and concise instructions on how to set up and use the hardware wallet securely, as well as educating users about the risks of phishing attacks, the importance of strong passwords, and other cybersecurity best practices.
5. Enhance Device Authenticity Verification

The Trezor data breach highlighted the importance of verifying the authenticity of a hardware wallet device. Manufacturers should invest in developing robust methods for users to verify the authenticity of their devices, such as unique identifiers, holographic seals, or secure verification codes. This will help users ensure that they are using genuine hardware wallets and mitigate the risk of falling victim to counterfeit devices.
In conclusion, the Trezor data breach serves as a stark reminder of the critical need for rigorous security measures in the hardware wallet industry. By prioritizing security audits, implementing multi-layered security, regular firmware updates, improving user education, and enhancing device authenticity verification, hardware wallet manufacturers can learn from this incident and better protect their users’ digital assets.
Q&A:
What happened in the Trezor data breach?
In the Trezor data breach, an attacker gained access to the Trezor servers and acquired sensitive user information, including email addresses.
How did the attacker gain access to the Trezor servers?
The method used by the attacker to gain access to the Trezor servers has not been disclosed by the company. However, it serves as a reminder to other hardware wallet manufacturers to maintain strong security protocols to protect against such breaches.
What information was compromised in the Trezor data breach?
The information compromised in the Trezor data breach included email addresses of users. It is important for users to be aware of the potential risks and take necessary precautions to protect their accounts and personal information.
What lessons can other hardware wallet manufacturers learn from the Trezor data breach?
The Trezor data breach highlights the importance for hardware wallet manufacturers to prioritize the security of their servers and user data. It is crucial to employ strong encryption protocols, regularly update security measures, and promptly respond to potential vulnerabilities or breaches.
What should users do to protect themselves following the Trezor data breach?
Following the Trezor data breach, users should take proactive steps to protect their accounts and personal information. This can include using strong, unique passwords, enabling two-factor authentication, regularly monitoring their accounts for any suspicious activity, and being cautious of phishing attempts.