Trezor Breach and the Rise in Phishing Attacks on Hardware Wallet Users

With the increasing popularity of cryptocurrencies, the need for secure storage solutions has become paramount. Hardware wallets, such as Trezor, have emerged as a popular choice for cryptocurrency users looking to protect their digital assets. These devices offer an additional layer of security by keeping private keys offline. However, a recent breach has highlighted the growing threat of phishing attacks on hardware wallet users.
Phishing attacks have long been a concern in the world of online security. These attacks involve tricking users into revealing sensitive information, such as passwords or private keys, by impersonating a legitimate website or service. While phishing attacks on hardware wallet users were once rare, they are now becoming more prevalent.
The recent breach involving Trezor, one of the most popular hardware wallet brands, has raised alarm bells within the cryptocurrency community. Hackers were able to create a convincing replica of the Trezor website and lure users into entering their private keys. This breach serves as a wake-up call for all hardware wallet users to remain vigilant and take necessary precautions.
Protecting oneself against phishing attacks requires a combination of awareness and technical measures. Users should be wary of any unsolicited communications or suspicious websites asking for their private keys. Additionally, enabling two-factor authentication and regularly updating firmware can help mitigate the risk of falling victim to a phishing attack.
The Importance of Protecting Your Cryptocurrency
With the increasing popularity of cryptocurrencies like Bitcoin and Ethereum, it is more important than ever to protect your digital assets. Cryptocurrency theft has become a growing concern as hackers and scammers continue to find new ways to exploit vulnerabilities in security systems.
1. Protect Against Phishing Attacks

Phishing attacks are one of the most common methods used by hackers to steal cryptocurrency. These attacks typically involve sending fake emails or messages that appear to be from a legitimate source, such as a hardware wallet manufacturer or a cryptocurrency exchange. The goal is to trick users into revealing their private keys or other sensitive information.
To protect yourself against phishing attacks, it is important to always double-check the legitimacy of any email or message you receive. Never click on suspicious links or download attachments from unknown sources. Additionally, enabling two-factor authentication (2FA) can provide an extra layer of security.
2. Use a Hardware Wallet

Using a hardware wallet is one of the most secure methods for storing your cryptocurrency. Unlike software wallets, which are vulnerable to hacking and malware attacks, hardware wallets store your private keys offline. This means that even if your computer or mobile device is compromised, your cryptocurrency remains safe.
When choosing a hardware wallet, make sure to purchase it directly from the manufacturer or an authorized reseller. Avoid buying used wallets or ones from unknown sources, as they may have been tampered with.
Remember: Your hardware wallet is only as secure as the measures you take to protect it. Be sure to set a strong PIN code and keep it in a safe place.
3. Stay Informed
Cryptocurrency is a rapidly evolving field, and it is essential to stay informed about the latest threats and security practices. Follow trusted sources, such as official hardware wallet manufacturers or cryptocurrency news outlets, to stay up-to-date with the latest information.
By staying informed and taking the necessary precautions, you can minimize the risk of falling victim to a phishing attack or other security breaches. Remember, protecting your cryptocurrency is ultimately your responsibility.
Common Techniques Used in Phishing Attacks

Phishing attacks have become increasingly sophisticated over the years, with hackers employing a variety of techniques to trick users into revealing their sensitive information. Here are some common methods used in phishing attacks:
1. Email Spoofing
Email spoofing involves the attacker sending an email that appears to be from a legitimate source, such as a well-known company or a trusted individual. The email is designed to deceive the recipient into disclosing their personal information, such as passwords or credit card details.
2. Website Spoofing
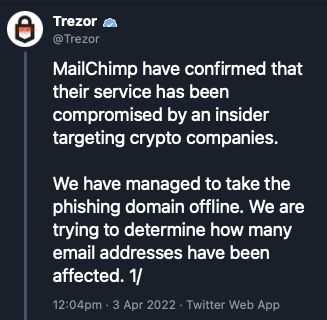
Website spoofing is a technique in which the attacker creates a fake website that closely resembles a legitimate website. The user is redirected to the fake website, where they are prompted to enter their login credentials or other sensitive information. The attacker can then use this information for malicious purposes.
3. Man-in-the-Middle Attacks

In a man-in-the-middle (MITM) attack, the attacker intercepts the communication between two parties, such as the user and the legitimate website. The attacker can then eavesdrop on the communication and collect any sensitive information exchanged, such as login credentials or financial details.
4. Malicious Attachments
Phishing emails often contain malicious attachments, such as infected PDF files or Word documents. When the user opens the attachment, malware is installed on their computer, allowing the attacker to gain unauthorized access or monitor their activities.
5. Smishing
Smishing, or SMS phishing, involves sending fraudulent text messages to trick users into revealing their personal information. These messages often claim to be from a legitimate organization, such as a bank, and provide a link or phone number for the user to contact.
6. Voice Phishing
Voice phishing, or vishing, is a technique in which the attacker impersonates a trusted entity over the phone. They may ask the victim to verify their account information or provide sensitive details, such as credit card numbers. The attacker can then use this information for fraudulent activities.
| Technique | Description |
|---|---|
| Email Spoofing | Sending fraudulent emails that appear to be from a legitimate source. |
| Website Spoofing | Creating fake websites that resemble legitimate ones to deceive users. |
| Man-in-the-Middle Attacks | Intercepting communication between users and legitimate websites to collect sensitive information. |
| Malicious Attachments | Sending phishing emails with infected attachments to install malware. |
| Smishing | Sending fraudulent text messages to trick users into revealing personal information. |
| Voice Phishing | Impersonating trusted entities over the phone to collect sensitive details. |
How to Safeguard Your Hardware Wallet from Phishing Attempts
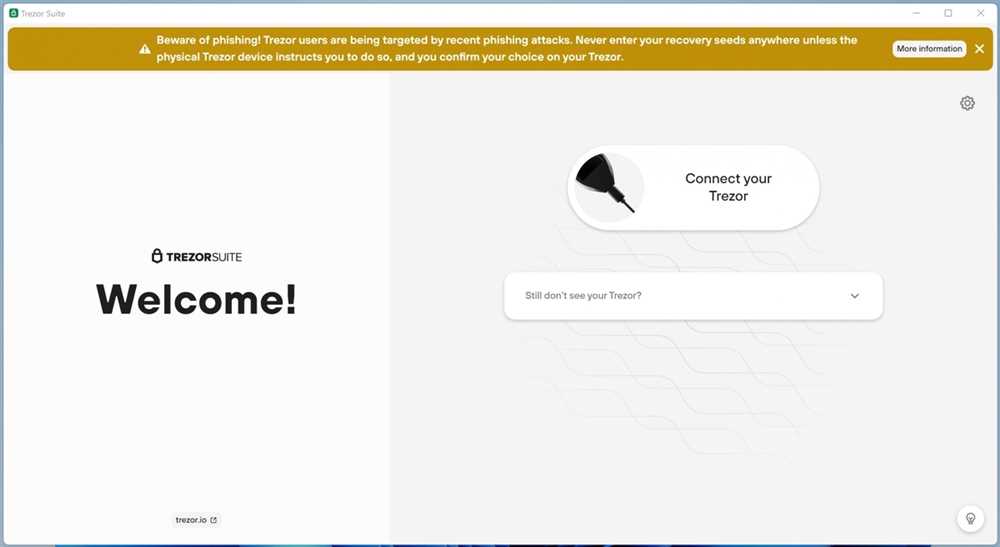
Phishing attacks on hardware wallet users are becoming increasingly sophisticated and prevalent. To protect your funds and personal information from falling into the wrong hands, it is essential to implement strong security measures. Follow these steps to safeguard your hardware wallet from phishing attempts:
| 1. Verify the legitimacy of the website: | Before entering any sensitive information, such as your wallet’s seed phrase or private keys, ensure that you are on the official website of your hardware wallet manufacturer. Double-check the URL, as phishing websites often use similar domain names or slightly altered spellings. |
| 2. Never click on suspicious links: | Avoid clicking on links from unknown sources or emails that ask you to provide personal information. Instead, manually type the URL into your browser or use bookmarks to access trusted websites. |
| 3. Enable two-factor authentication (2FA): | Activate 2FA on your hardware wallet to add an extra layer of security. This way, even if phishers obtain your wallet’s password, they would still need physical access to your device to complete the login process. |
| 4. Update your firmware regularly: | Hardware wallet manufacturers frequently release firmware updates to address security vulnerabilities. Stay up-to-date by regularly checking for and installing the latest firmware versions. |
| 5. Never share your seed phrase or private keys: | Hardware wallets are designed to keep your seed phrase and private keys offline. Never share this information with anyone and store it securely offline. Be cautious of anyone asking for your seed phrase, even if they claim to be from customer support. |
| 6. Use strong and unique passwords: | Create complex and unique passwords for your hardware wallet accounts. Avoid using passwords that are easy to guess or that you have used for other online accounts. |
| 7. Educate yourself about phishing techniques: | Stay informed about the latest phishing techniques used by scammers. Be skeptical of emails, messages, or websites that ask for your personal information, especially if they create a sense of urgency or offer unrealistic rewards. |
| 8. Keep your computer and software updated: | Regularly update your computer’s operating system and security software to protect against malware and other cyber threats. Use reputable antivirus software and enable automatic updates. |
| 9. Keep a backup of your wallet: | Create a backup of your wallet’s seed phrase and store it in a secure location separate from your hardware wallet. This way, even if your device is compromised or lost, you can easily recover your funds. |
| 10. Be cautious of public Wi-Fi networks: | Avoid accessing your hardware wallet or entering sensitive information when connected to public Wi-Fi networks. These networks are often unsecured, which makes it easier for attackers to intercept your data. |
By following these security measures, you can significantly reduce the risk of falling victim to phishing attacks and keep your hardware wallet and funds safe.
Question-answer:
What is a hardware wallet?
A hardware wallet is a physical device that is used to store and manage cryptocurrency private keys offline. It provides an extra layer of security compared to software wallets that are connected to the internet.
What is a phishing attack?
A phishing attack is a type of cyber attack where the attacker disguises themselves as a trustworthy entity in order to trick individuals into revealing sensitive information, such as passwords or financial information. In the context of hardware wallet users, the attacker might send a fake email or create a fake website that looks similar to the official hardware wallet platform, in an attempt to steal the user’s private keys.
How can I protect myself from phishing attacks on hardware wallets?
To protect yourself from phishing attacks on hardware wallets, it is important to always verify the authenticity of any communication or website related to your hardware wallet. This can be done by double-checking the email sender’s address, ensuring that the website’s URL is correct, and being cautious of any unsolicited or suspicious requests for personal information.
What should I do if I suspect I have fallen victim to a phishing attack?
If you suspect that you have fallen victim to a phishing attack, it is crucial to act quickly. Immediately disconnect your hardware wallet from any connected devices, change all passwords associated with your cryptocurrency accounts, and contact the official support team of your hardware wallet provider. They will be able to guide you through the necessary steps to secure your funds and prevent any further unauthorized access.