The Hacking Challenge: Testing the Security of Trezor

As the use of cryptocurrencies continues to grow, so does the need for secure storage solutions. One of the most popular hardware wallets on the market is Trezor, known for its robust security measures and user-friendly interface. But just how secure is Trezor? In order to put it to the test, a hacking challenge was organized to assess its vulnerabilities and determine if it truly lives up to its reputation.
With the rise of cyber attacks and the potential loss of digital assets, it is crucial to ensure that hardware wallets like Trezor provide the necessary protection. During the hacking challenge, a team of skilled hackers and security experts were tasked with attempting to gain access to the wallet and steal its contents. The challenge aimed to identify any weaknesses in Trezor’s security system and provide valuable insights for improvement.
Throughout the challenge, the hackers utilized various methods and techniques to bypass Trezor’s security measures. They tried to exploit potential vulnerabilities, such as physical tampering, software vulnerabilities, and social engineering tactics. Each attempt was meticulously documented and analyzed to gauge the effectiveness of Trezor’s protection mechanisms.
The results of the hacking challenge were both insightful and reassuring. Despite the numerous attempts made by the hackers, Trezor’s security proved to be highly robust. The experts were unable to gain unauthorized access to the wallet or compromise its contents. This outcome attests to the strength of Trezor’s security design and highlights its efficacy in safeguarding digital assets.
In conclusion, the hacking challenge served as a valuable exercise to assess the security of Trezor, one of the leading hardware wallets in the cryptocurrency market. The challenge showcased the wallet’s resilience against various hacking techniques and attests to its ability to protect users’ funds. With the continuous advancements in technology and the ever-evolving threat landscape, it is vital for hardware wallets like Trezor to regularly undergo rigorous testing to ensure their users’ assets remain secure.
Hacking Trezor’s Security Measures
As one of the most popular hardware wallets in the cryptocurrency world, Trezor is known for its robust security measures. However, no system is perfect, and this article will explore some potential vulnerabilities in Trezor’s security.
Brute Force Attacks

One of the simplest ways to hack into a system is by using a brute force attack. In the case of Trezor, this involves systematically guessing the PIN or recovery seed until the correct combination is found. While Trezor has implemented measures to prevent brute force attacks, such as a limited number of attempts and enforced delays after multiple failed tries, there is still a small possibility that an attacker could successfully guess the PIN or seed.
Physical Access

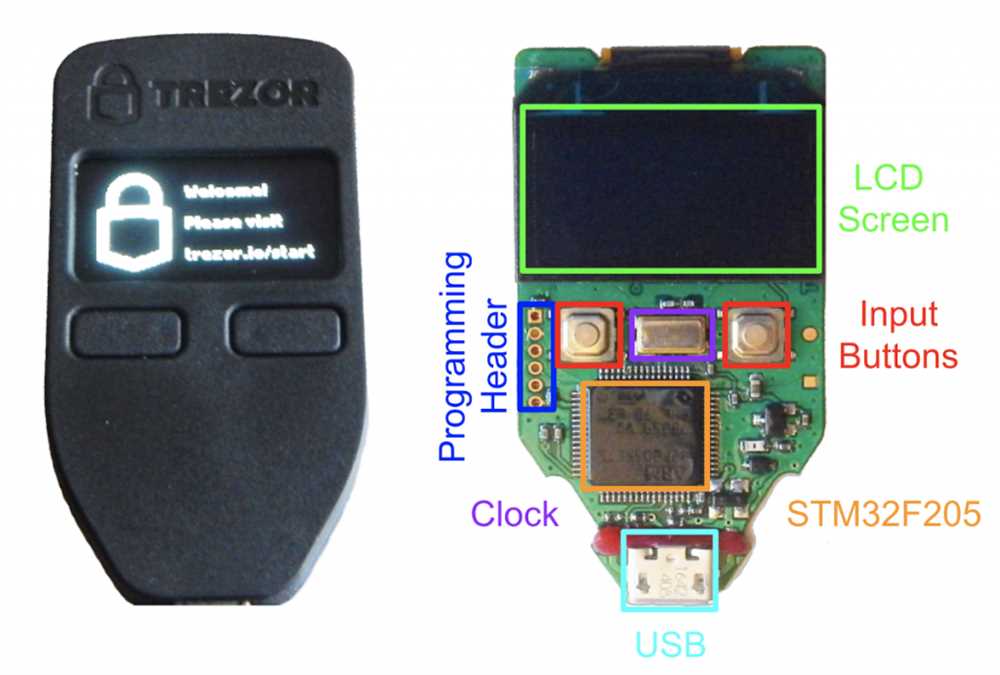
Another aspect to consider when assessing the security of Trezor is physical access to the device. Although Trezor devices are designed to be tamper-proof and have built-in protections against physical attacks, it is still possible for a skilled attacker to gain access to the device. This could involve techniques such as microprobing, which allows the attacker to directly access the device’s memory and extract sensitive information.
It is important for Trezor users to keep their devices in a secure location and be cautious about sharing any information about their wallets. Additionally, regularly updating the firmware and following best practices for securing cryptocurrencies can help minimize the risk of physical attacks.
Overall, while Trezor has taken significant steps to protect user wallets and prevent hacking attempts, it is crucial for users to remain vigilant and educated about potential security risks.
Understanding the Vulnerabilities
When it comes to testing the security of Trezor, it’s important to understand the potential vulnerabilities that could be exploited by hackers. By identifying these weaknesses, we can better protect user funds and ensure the integrity of the device.
Physical Attacks
One potential vulnerability is physical attacks. These attacks involve gaining physical access to the device and attempting to extract sensitive information or tamper with the hardware. For example, an attacker could try to extract the firmware from the device or physically modify the hardware to gain unauthorized access.
To secure against physical attacks, Trezor uses tamper-evident seals and secure elements. The tamper-evident seals are designed to show signs of tampering if someone tries to open the device. The secure elements are hardened chips that protect the sensitive data and ensure that it cannot be easily extracted.
Software Attacks
Another area of vulnerability is software attacks. These attacks exploit weaknesses in the device’s software or firmware to gain unauthorized access or extract sensitive information. Examples of software attacks include malware or phishing attacks.
Trezor mitigates software attacks by using a secure bootloader and signed firmware updates. The secure bootloader ensures that only authentic firmware can be installed on the device, preventing malicious code from running. Additionally, Trezor uses a strong encryption algorithm to protect user data, making it difficult for hackers to extract sensitive information.
Understanding these vulnerabilities is crucial in testing the security of Trezor. By identifying and addressing potential weaknesses, we can create a more robust and secure device that protects user funds and ensures the integrity of the cryptocurrency ecosystem.
Trezor’s Encryption Techniques
Trezor is a popular hardware wallet designed to keep cryptocurrencies secure. One key component of its security is the encryption techniques it employs to protect sensitive data.
Encryption is a process of converting plain text into encoded data that can only be decoded with a specific key or password. Trezor uses several encryption techniques to safeguard users’ private keys and other sensitive information:
1. Symmetric Encryption: Trezor utilizes symmetric encryption algorithms such as AES (Advanced Encryption Standard) to encrypt and decrypt data. With symmetric encryption, the same key is used for both encryption and decryption. This ensures that only authorized individuals with the correct key can access the data stored on the device.
2. Public Key Cryptography: Trezor also employs public key cryptography for secure communication and key management. Public key cryptography utilizes a pair of keys: a public key for encryption and a private key for decryption. The receiver’s public key is used to encrypt data, while the private key is kept securely stored on the Trezor device for decryption.
3. Hierarchical Deterministic (HD) Wallets: Trezor uses HD wallets, which provide an additional layer of security. HD wallets derive multiple cryptographic key pairs from a single, randomly generated seed. This means that users only need to remember one seed phrase to access a virtually unlimited number of private keys. HD wallets also make it easier to create secure backups of the wallet.
4. Shamir’s Secret Sharing: Trezor incorporates Shamir’s Secret Sharing algorithm to prevent single points of failure. Shamir’s Secret Sharing divides a secret into multiple parts, or “shares,” which are distributed among different parties. A specified number of shares is required to reconstruct the secret. This ensures that even if one share is compromised, the secret remains secure.
5. Password-Based Encryption: In addition to the above techniques, Trezor allows users to set up a password for an extra layer of protection. This password is used to encrypt the device’s storage, adding an additional level of security to the encrypted data.
Through a combination of symmetric encryption, public key cryptography, HD wallets, Shamir’s Secret Sharing, and password-based encryption, Trezor ensures the security of users’ cryptocurrencies and sensitive data. Understanding these encryption techniques can help users make informed decisions when it comes to securing their digital assets.
Penetration Testing and Risk Assessment
Penetration testing, also known as ethical hacking, is a process used to evaluate the security measures of a system or network. This testing is conducted by security experts who attempt to exploit vulnerabilities in order to assess the level of risk associated with a system.
The main purpose of penetration testing is to identify weaknesses and assess the potential impact of a successful cyber attack. It involves simulating real-world attacks in a controlled environment to identify potential vulnerabilities that could be exploited by malicious actors.
Risk assessment, on the other hand, is the process of analyzing and evaluating potential risks in order to determine the likelihood and impact of those risks. It involves identifying threats, vulnerabilities, and the potential consequences of a security breach.
Both penetration testing and risk assessment are critical components of ensuring the security and resilience of a system or network. By conducting thorough penetration testing, organizations can proactively identify and address vulnerabilities before they can be exploited by hackers.
A well-executed penetration test can provide valuable insights into the security posture of a system, highlight any weaknesses, and help organizations prioritize remediation efforts. It also helps organizations comply with industry regulations and standards by demonstrating an ongoing commitment to security.
Risk assessment, on the other hand, helps organizations understand their risk profile and make informed decisions about resource allocation and risk mitigation strategies. By identifying and quantifying risks, organizations can effectively allocate resources to address the most critical vulnerabilities.
Both penetration testing and risk assessment require a combination of technical expertise, analytical skills, and a deep understanding of potential threats and vulnerabilities. Organizations should consider engaging certified professionals with experience in these areas to perform comprehensive security assessments.
By incorporating both penetration testing and risk assessment into their security practices, organizations can minimize the potential impact of cyber attacks and protect their assets, data, and reputation.
Preventing Hacking Attempts on Trezor Wallet
Hacking attempts on cryptocurrency wallets, such as the Trezor wallet, have become increasingly common. As a user, it is crucial to take measures to protect your digital assets and prevent hackers from gaining unauthorized access to your funds. Here are some steps you can take to enhance the security of your Trezor wallet:
1. Enable Two-Factor Authentication (2FA)

Two-factor authentication adds an extra layer of security to your Trezor wallet by requiring a second verification step, typically a unique code generated on your smartphone. This ensures that even if a hacker manages to obtain your password, they still won’t be able to access your wallet without the secondary code. Enable 2FA to make it significantly harder for hackers to breach your wallet’s security.
2. Regularly Update Firmware
Trezor regularly releases firmware updates to fix security vulnerabilities and improve the overall performance of its wallets. Make sure to regularly check for firmware updates and install them promptly. These updates often include important security patches that can help prevent hacking attempts.
3. Be Cautious of Phishing Attempts
Phishing attempts are one of the most common methods used by hackers to gain access to your wallet. Always double-check the authenticity of the website or application you are using to access your Trezor wallet. Be cautious of any suspicious links or emails requesting your login credentials or private keys. Trezor will never ask for such information directly.
4. Use Strong and Unique Passwords
Creating a strong and unique password is essential to protect your Trezor wallet. Avoid using common passwords or personal information that can be easily guessed or hacked. Consider using a password manager to generate and store strong and unique passwords for all your online accounts, including your Trezor wallet.
5. Keep Your Seed Phrase Secure
The seed phrase is a crucial component of your Trezor wallet’s security. It acts as a backup in case you lose access to your wallet. Make sure to write down your seed phrase and keep it in a secure location, such as a safe or a safety deposit box. Never share your seed phrase with anyone, as it can be used to gain unauthorized access to your wallet.
By following these precautions, you can significantly reduce the risk of your Trezor wallet being hacked. Remember that the security of your digital assets ultimately depends on your actions, so always stay vigilant and proactive in protecting your funds.
Implementing Two-Factor Authentication
In order to enhance the security of the Trezor device, two-factor authentication (2FA) can be implemented. Two-factor authentication adds an extra layer of security by requiring users to provide two separate forms of identification: something they know (password) and something they have (usually a mobile device).
The first step in implementing 2FA is to integrate a reliable authentication service into the Trezor software. There are several popular authentication services available, such as Google Authenticator and Authy. These services generate a unique code that the user must enter along with their password to log in.
Once the authentication service is integrated, users can set up 2FA for their Trezor device. This typically involves scanning a barcode with their mobile device using an authentication app. The app then generates a unique code that is synced with the Trezor device.
When logging in, users will be prompted to enter their password as usual. Once the password is entered, the Trezor device will prompt the user to enter the unique code generated by the authentication app on their mobile device. This ensures that even if a hacker obtains the user’s password, they cannot gain access to the Trezor device without also having physical possession of the user’s mobile device.
It is important for users to keep their mobile devices secure as well. They should enable passcodes or biometric authentication on their devices to prevent unauthorized access. Additionally, users should enable any available security features, such as remote wiping, in case their device is lost or stolen.
By implementing two-factor authentication, Trezor can greatly enhance the security of their devices and protect their users’ assets. While no security measure is foolproof, 2FA adds an extra layer of protection that can make it significantly more difficult for hackers to gain unauthorized access.
Question-answer:
Is Trezor’s security really trustworthy?
Yes, Trezor’s security is highly trustworthy. It has undergone rigorous testing and has never been breached. It utilizes multiple layers of encryption and authentication to protect users’ funds.
How can I test the security of my Trezor device?
To test the security of your Trezor device, you can participate in hacking challenges like the one described in the article. These challenges are designed to simulate real-world attacks and help evaluate the device’s resilience against hacking attempts.
What happens if someone gains physical access to my Trezor device?
If someone gains physical access to your Trezor device, they would still need to know your PIN code to access your funds. After a certain number of failed attempts, the device wipes itself clean, ensuring that unauthorized users cannot gain access to your private keys.