Weaknesses in Hardware Wallets Exposed by the Trezor Breach

Hardware wallets have long been touted as one of the safest ways to store cryptocurrencies. With their offline storage and robust security features, these devices have become the go-to solution for many crypto investors. However, a recent breach of the popular Trezor wallet has exposed some significant weaknesses in these supposedly impenetrable devices.
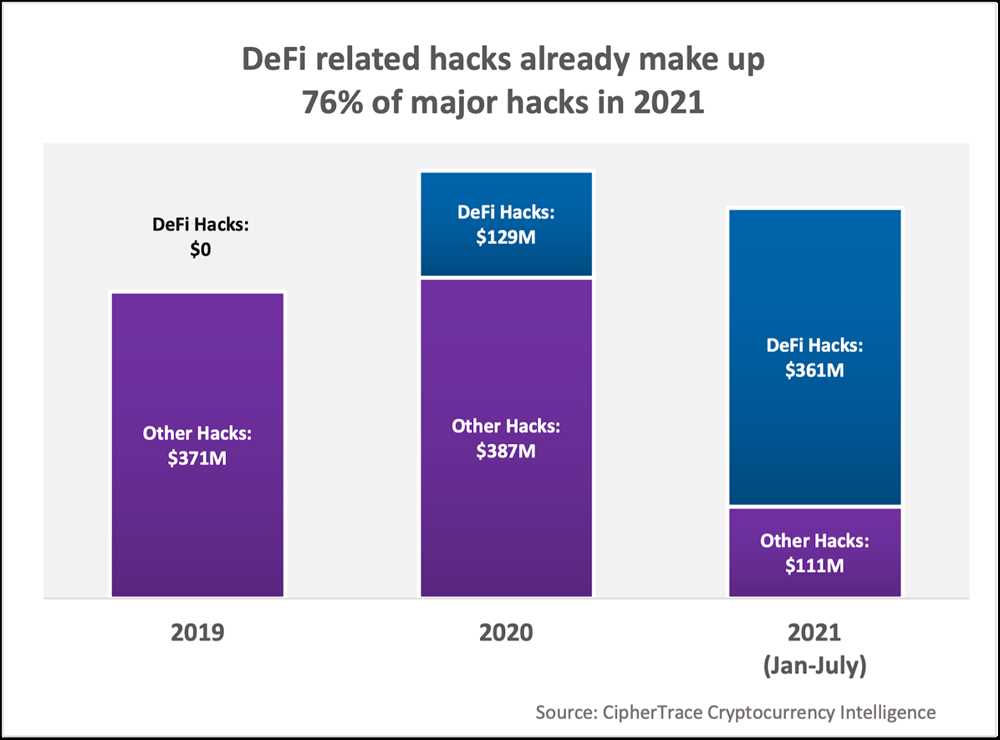
In January 2021, a group of hackers known as “Kraken” managed to exploit a vulnerability in Trezor’s firmware, gaining unauthorized access to users’ private keys. This breach allowed the attackers to potentially steal funds from unsuspecting users’ wallets. It was a wake-up call for the cryptocurrency community, highlighting the importance of regularly updating firmware and remaining vigilant against potential threats.
The Trezor breach shed light on the inherent vulnerabilities of hardware wallets. Despite their advanced security measures, these devices are not immune to hacking attempts. The incident served as a reminder that security is an ongoing process, and even the most reputable products can be compromised.
One of the main concerns raised by the Trezor breach is the potential for physical attacks on hardware wallets. While hardware wallets provide an extra layer of protection by keeping private keys offline, they are still susceptible to manipulation if they fall into the wrong hands. Sophisticated attackers can tamper with the device’s hardware or use specialized tools to extract sensitive information.
The incident also highlighted the importance of open-source firmware in hardware wallets. Trezor’s firmware, although widely regarded as secure, contained a vulnerability that hackers were able to exploit. This revelation brought into question the integrity of closed-source firmware used by other hardware wallet manufacturers. Open-source firmware allows the community to review the code and identify potential vulnerabilities, making it more difficult for hackers to exploit.
While the Trezor breach was undoubtedly a setback for hardware wallets, it also served as a catalyst for the industry to improve its security measures. Manufacturers have since implemented firmware updates to address the vulnerability exposed by the breach. Additionally, more emphasis is being placed on rigorous code reviews, bug bounties, and ongoing vulnerability assessments.
As cryptocurrency continues to gain mainstream adoption, the security of hardware wallets will remain a critical consideration. While no system is entirely infallible, the Trezor breach has prompted the industry to reevaluate and strengthen its security practices. Users are now more aware of the potential risks and are taking proactive steps to protect their funds.
The Trezor Breach: Revealing Vulnerabilities in Hardware Wallets

In recent years, hardware wallets have become increasingly popular among cryptocurrency users as a secure way to store their digital assets. These devices offer an additional layer of protection by keeping private keys offline, making them less vulnerable to online attacks. However, the security of hardware wallets came into question when the Trezor breach occurred.
The Trezor breach revealed significant vulnerabilities in hardware wallets, raising concerns among cryptocurrency investors and enthusiasts. Users of Trezor hardware wallets were shocked to discover that a hacker managed to gain access to sensitive information, including private keys.
One of the main weaknesses that the Trezor breach exposed was the vulnerability of the physical device itself. Despite being designed to be tamper-proof, skilled hackers were able to exploit flaws in the hardware and gain unauthorized access to the device. This highlights the importance of regular security audits and continuous improvement in hardware wallet designs.
Another key vulnerability was the lack of a secondary authentication method. Many hardware wallets, including the affected Trezor devices, rely solely on a single factor authentication, such as a PIN. However, if a hacker manages to obtain the PIN, they can easily access the device’s contents. Adding a second layer of authentication, such as biometric verification or a password, can significantly enhance the security of hardware wallets.
The Trezor breach also highlighted the importance of firmware updates. The hacked devices were running outdated firmware versions, which contained known vulnerabilities that were exploited by the attacker. It is crucial for hardware wallet manufacturers to regularly release firmware updates that address security flaws and vulnerabilities, and for users to promptly install these updates to ensure the highest level of protection.
Furthermore, the incident shed light on the risks associated with counterfeit hardware wallets. In some cases, unsuspecting users purchased fake devices that were infected with malware, allowing hackers to gain unauthorized access to their digital assets. It is essential for users to purchase hardware wallets directly from reputable sources and verify the authenticity of the device before using it.
| Vulnerabilities | Recommendations |
|---|---|
| Physical device vulnerabilities | Regular security audits and continuous improvement in hardware wallet designs |
| Lack of secondary authentication | Add a second layer of authentication, such as biometric verification or a password |
| Outdated firmware | Regularly release firmware updates that address security flaws and vulnerabilities |
| Risks of counterfeit hardware wallets | Purchase hardware wallets directly from reputable sources and verify authenticity |
The Trezor breach was a wake-up call for the cryptocurrency community, highlighting the need for constant vigilance and improvement in the security of hardware wallets. By addressing the vulnerabilities exposed by the breach and implementing the recommended measures, users can better protect their digital assets and ensure a safer cryptocurrency experience.
Understanding the Security Flaws in Hardware Wallets

Hardware wallets have long been regarded as one of the most secure methods for storing and transacting cryptocurrencies. With their offline storage and robust encryption protocols, these devices offer users peace of mind. However, recent events, such as the Trezor breach, have exposed vulnerabilities in hardware wallets that should not be overlooked.
The Human Element

One of the inherent security flaws in hardware wallets lies with the human element. While these devices offer a higher level of security compared to software wallets, they still rely on users to follow best practices. It is crucial for users to generate a strong, unique PIN and keep it private. Furthermore, users should ensure that they are purchasing their hardware wallets from reputable sources to avoid tampered devices that could compromise the security of their funds.
Additionally, users must exercise caution when interacting with their hardware wallets. Phishing attacks and malware can still pose a threat to the security of hardware wallets. Users should double-check the authenticity of any communication received from their wallet provider and be wary of any suspicious activity.
Supply Chain Attacks

Another security vulnerability that hardware wallets face is supply chain attacks. This type of attack occurs when malicious actors tamper with the hardware wallet during the manufacturing and distribution process. By injecting malware or compromising the device’s firmware, attackers can gain unauthorized access to users’ funds.
To mitigate the risk of supply chain attacks, hardware wallet manufacturers must implement strict security measures throughout the production and distribution chain. Independent audits, secure distribution channels, and tamper-evident packaging can help minimize the possibility of compromised devices reaching the hands of end-users.
Furthermore, users can enhance their security by verifying the authenticity of the hardware wallet they receive. Checking the packaging for signs of tampering, scanning for firmware updates from official sources, and researching the reputation of the manufacturer are all crucial steps to ensure the integrity of the device.
In conclusion, while hardware wallets offer significant advantages in terms of security, they are not immune to flaws and vulnerabilities. Users must be mindful of the human element and practice good security hygiene. Manufacturers must also take responsibility for implementing robust security measures throughout the supply chain to minimize the risk of compromise.
Lessons Learned from the Trezor Breach

The Trezor breach served as a wake-up call for the hardware wallet industry, highlighting several crucial lessons that need to be learned and implemented. Here are some of the key takeaways from this incident:
1. The Importance of Continuous Security Audits

One of the main lessons is that hardware wallet manufacturers should prioritize continuous security audits. These audits should be performed by third-party experts to identify any vulnerabilities or weaknesses in the device’s architecture. By conducting regular audits, manufacturers can ensure that their products are up-to-date and well-protected against emerging threats.
2. Clear Communication with Users
The breach revealed the importance of clear and transparent communication between hardware wallet manufacturers and their users. In the event of a security breach or vulnerability, it is crucial for manufacturers to promptly notify their users and provide clear instructions on how to mitigate the risks. Transparent and timely communication fosters trust and allows users to take necessary precautions to safeguard their funds.
3. Enhanced Firmware Security

The Trezor breach highlighted the need for enhanced firmware security. Firmware updates should be thoroughly tested and validated before being released to the public. Manufacturers must prioritize rigorous testing protocols and ensure that no vulnerabilities are introduced during the firmware update process.
4. Two-Factor Authentication

Implementing two-factor authentication (2FA) can significantly enhance the security of hardware wallets. By requiring users to authenticate themselves through an additional device or method, such as a smartphone app or biometric verification, the risk of unauthorized access to the wallet can be greatly reduced.
5. Regularly Updating Security Measures
Hardware wallet manufacturers need to stay proactive in updating their security measures regularly. This includes implementing the latest encryption technologies, adopting robust password policies, and keeping up with industry best practices. By continuously improving security measures, manufacturers can stay ahead of potential threats and better protect their users’ assets.
In conclusion, the Trezor breach shed light on several important lessons for the hardware wallet industry. By emphasizing continuous security audits, transparent communication, enhanced firmware security, implementing two-factor authentication, and regularly updating security measures, manufacturers can strengthen the overall security of hardware wallets and better safeguard user funds.
Strengthening Hardware Wallets: The Way Forward

After the Trezor breach highlighted vulnerabilities in hardware wallets, it has become crucial for the industry to focus on strengthening the security of these devices. Here are some key steps that can be taken to enhance the security of hardware wallets:
1. Continuous Testing and Auditing: Regular security testing and independent audits should be conducted to identify and address any vulnerabilities or weaknesses in hardware wallets. This will help ensure that the devices are resilient to attacks and that any potential issues are mitigated in a timely manner.
2. Multi-Factor Authentication: Implementing multi-factor authentication protocols can add an extra layer of security to hardware wallets. This could involve requiring the user to provide more than one piece of verification, such as a password and a biometric scan, before granting access to the wallet.
3. Secure Element Integration: Hardware wallets should incorporate secure elements, such as trusted execution environments or secure chips, to protect sensitive information and cryptographic operations. This can help safeguard against physical attacks and ensure that private keys remain secure even if the device is compromised.
4. Firmware and Software Updates: Manufacturers should prioritize regular firmware and software updates to address any newly discovered vulnerabilities or add new security features. Users should also be encouraged to keep their devices up to date to benefit from these improvements.
5. User Education and Best Practices: Educating users about the proper usage and best practices for hardware wallets is crucial. This includes guidance on securely storing recovery seeds, protecting devices from physical tampering, and avoiding phishing attacks. By fostering a security-conscious user base, the overall security of hardware wallets can be significantly enhanced.
By implementing these measures and continuously researching and developing new security solutions, the technology industry can work towards creating hardware wallets that are more robust and resistant to attacks. Strengthening hardware wallets is paramount in ensuring the safety and security of cryptocurrency assets for both individual users and organizations alike.
Q&A:
What is the Trezor Breach?
The Trezor Breach refers to a security incident that occurred with the Trezor hardware wallet, where a group of attackers gained physical access to the device and were able to exploit vulnerabilities in its security features.
What weaknesses in hardware wallets did the Trezor Breach expose?
The Trezor Breach exposed certain weaknesses in hardware wallets, such as the susceptibility to physical attacks when an attacker has physical access to the device. It also highlighted the importance of securely storing backup seeds and utilizing strong PIN codes to protect against unauthorized access.