Are There Any Exploits in Trezor One’s Security System? A Critical Analysis

Trezor One is one of the most popular hardware wallets used for securing cryptocurrencies. Its robust security system is known for providing an extra layer of protection to users’ digital assets. However, no system is perfect, and Trezor One is no exception. In this article, we will conduct a comprehensive analysis of Trezor One’s security system and explore its potential exploits and vulnerabilities.
One of the key features of Trezor One’s security system is its secure element chip, which is responsible for storing the private keys of the users. This chip is designed to be resistant to physical tampering and extraction of sensitive data. However, recent studies have shown that even this highly secure chip is not immune to attacks. Vulnerabilities such as side-channel attacks and fault injections can potentially compromise the security of the private keys stored in the chip.
Another aspect of Trezor One’s security system that is worth analyzing is its firmware. The firmware is regularly updated by the manufacturer to fix any identified vulnerabilities and improve the overall security of the device. However, as with any software, there is always a risk of undiscovered bugs or flaws that can be exploited by malicious actors. It is crucial for users to keep their firmware up to date to benefit from the latest security patches.
Furthermore, the relationship between the user and the hardware wallet itself introduces another potential vulnerability. While Trezor One is designed to prevent unauthorized access to the private keys, it relies on the user’s actions to ensure the security of their digital assets. Social engineering attacks, such as phishing emails or physical coercion, can trick users into revealing their private keys or performing unauthorized transactions.
In conclusion, while Trezor One offers a high level of security for storing cryptocurrencies, it is important to be aware of its potential vulnerabilities. Users should stay vigilant and keep their firmware up to date, be cautious of social engineering attacks, and exercise best practices for securing their digital assets.
Overview of Trezor One’s Security System
Trezor One is a hardware wallet designed to securely store cryptocurrencies. Its security system is built to protect user’s private keys and ensure the safety of their digital assets.
Offline Storage

One of the key security features of Trezor One is its ability to generate and store private keys offline. The device uses a random number generator to create secure private keys, which are then stored in the device’s secure element. This means that even if the device is connected to a compromised computer, the private keys remain safe.
Secure Display

Trezor One has a built-in display that is used to verify transactions. This ensures that the user can double-check the details of the transaction, such as the recipient address and the amount, before approving it. By providing a secure display, Trezor One protects users from phishing attacks and unauthorized transactions.
Pin Code and Recovery Seed
Trezor One requires users to set up a pin code during the initial setup process. This pin code is used to authenticate the user and prevent unauthorized access to the device. In addition, Trezor One generates a recovery seed, which consists of a series of 24 words. This seed can be used to restore access to the wallet in case the device is lost or damaged.
By combining the pin code and recovery seed, Trezor One ensures that even if the device is stolen, an attacker would need both the physical device and the recovery seed to gain access to the user’s funds.
Firmware Verification
Trezor One’s firmware is open-source, allowing the community to review and verify its security. The device uses a secure bootloader to ensure that only signed firmware updates can be installed. This prevents malicious actors from tampering with the device’s firmware and compromising its security.
In addition, Trezor One uses a secure communication protocol with the host computer, ensuring that the device’s firmware cannot be manipulated during the transaction signing process.
Overall, Trezor One’s security system provides robust protection against common attack vectors, such as phishing, malware, and physical theft. By combining offline storage, a secure display, pin code, recovery seed, and firmware verification, Trezor One offers users a reliable hardware wallet solution for managing their cryptocurrencies.
Exploring the Exploits in Trezor One

Trezor One is a popular hardware wallet that provides a secure way to store and manage cryptocurrencies. However, like any other technology, it is not completely immune to vulnerabilities and exploits. In this section, we will explore some of the known exploits in Trezor One and the potential risks they pose to its security system.
1. Side-channel attacks:

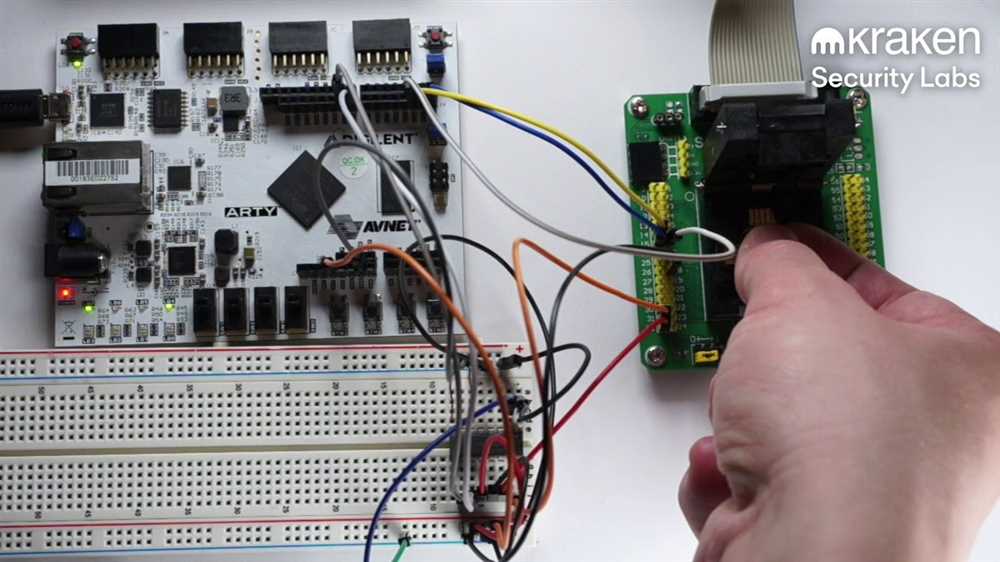
One of the major concerns in hardware security is side-channel attacks. Attackers can exploit variations in power consumption, electromagnetic emissions, or even timing to gain information about sensitive data processed by the device. Trezor One is vulnerable to side-channel attacks, particularly through power analysis and electromagnetic radiation analysis. By carefully analyzing these side channels, attackers could potentially extract sensitive information such as the private keys stored in the wallet.
2. Physical tampering:

Trezor One wallets are designed to be tamper-resistant, but they are not entirely tamper-proof. Given enough time, resources, and expertise, an attacker could physically tamper with the device to gain unauthorized access to the sensitive information stored within. This could involve dismantling the wallet, accessing the internal components, and bypassing any physical security measures implemented. Trezor One does provide measures to detect physical tampering, such as anti-tamper seals, but advanced attackers may still find ways to overcome these barriers.
Note: It is important to mention that physical tampering requires physical access to the device, making it less likely for remote attacks.
3. Supply chain attacks:

Supply chain attacks involve injecting malicious code or components into a product during the manufacturing or distribution process. If an attacker gains access to the supply chain of Trezor One, they could compromise the security of the hardware wallet. This could involve implanting a backdoor, modifying the firmware, or tampering with the device before it reaches the end-user. Supply chain attacks are difficult to detect and can potentially affect a large number of devices.
Conclusion: While Trezor One is generally considered a secure hardware wallet, it is important for users to be aware of the potential exploits and vulnerabilities that exist. By understanding these risks, users can take appropriate measures to protect their cryptocurrencies and ensure the security of their Trezor One wallets.
Identifying Vulnerabilities in Trezor One’s Security

Trezor One is a widely used hardware wallet that provides secure storage for cryptocurrencies. However, no security system is perfect, and it is essential to identify vulnerabilities to ensure the safety of users’ funds and personal information. This section will discuss some potential vulnerabilities in the security system of Trezor One.
1. Physical vulnerabilities
One possible vulnerability is the physical access to the device. If an attacker gains physical access to the Trezor One, they may attempt to extract sensitive information or tamper with the device to gain unauthorized access to funds. This highlights the importance of safeguarding the physical security of the hardware wallet.
2. Firmware vulnerabilities
Firmware is the software embedded in the hardware wallet that controls its operations. Vulnerabilities in the firmware can be exploited to gain unauthorized access or perform malicious activities. Trezor One regularly releases firmware updates to address any identified vulnerabilities and improve security. However, it is crucial for users to promptly update their devices to the latest firmware version to protect against potential exploits.
3. Side-channel attacks
Side-channel attacks exploit information leaked through unintended channels, such as power consumption or electromagnetic emissions, to gain unauthorized access to the device. Although Trezor One implements countermeasures to mitigate side-channel attacks, it is essential to stay vigilant and monitor for any potential weaknesses in the system.
4. Supply chain attacks
Supply chain attacks involve tampering with the device during the manufacturing or distribution process. An attacker may introduce malicious components or manipulate the firmware to compromise the security of the device. To mitigate the risk of supply chain attacks, it is essential to purchase hardware wallets directly from trusted sources and verify the authenticity of the device.
Identifying vulnerabilities in the security system of Trezor One is crucial to ensure the ongoing protection of users’ funds and information. By addressing and patching any vulnerabilities promptly, the security of Trezor One can be further enhanced, providing users with peace of mind when storing their cryptocurrencies.
Q&A:
What is the security system of Trezor One?
Trezor One has a multi-layered security system. It includes hardware encryption, a secure boot process, and passphrase protection.
What are the exploits and vulnerabilities found in Trezor One’s security system?
There have been several exploits and vulnerabilities found in Trezor One’s security system. Some of them include physical attacks, side-channel attacks, and firmware vulnerabilities.