Exploring the Security Vulnerabilities Exposed by the Trezor Breach

In today’s digital age, protecting our financial assets and ensuring the security of our personal information has become paramount. With the rise of cryptocurrencies, individuals have turned to hardware wallet devices like the Trezor to safeguard their digital assets. However, recent events have brought attention to potential security vulnerabilities in this popular hardware wallet.
The Trezor breach, which occurred in the not-too-distant past, exposed a critical flaw in the device’s security system. This breach served as a wake-up call to both Trezor users and hardware wallet manufacturers alike, highlighting the importance of constant vigilance and the need for continuous improvement in security measures.
One of the primary vulnerabilities identified in the Trezor breach was a weakness in its firmware. Malicious actors were able to exploit this weakness and gain unauthorized access to users’ wallets, potentially compromising their cryptocurrency holdings. The consequences of such a breach are far-reaching, as it not only puts individuals’ financial security at risk but also undermines the trust and credibility of hardware wallet solutions.
Another significant security vulnerability revealed by the Trezor breach was the physical accessibility of the device. While the Trezor’s main selling point is its offline storage capability, this breach brought attention to the fact that physical access to the hardware wallet could potentially compromise its security. This revelation has prompted users and manufacturers to consider additional layers of protection such as tamper-evident seals or biometric authentication.
The Trezor breach serves as a reminder that no security system is foolproof, and constant efforts are required to stay steps ahead of potential threats. Hardware wallet manufacturers must remain dedicated to strengthening their security protocols, while users must also remain vigilant and take necessary precautions to protect their digital assets. By closely examining the vulnerabilities exposed in the Trezor breach, we can gain valuable insights into the evolving security landscape and work towards creating more robust and secure solutions for the future.
Exploring Security Vulnerabilities
Security vulnerabilities in systems can lead to devastating consequences. In the case of the Trezor breach, it is important to delve into the vulnerabilities that were exploited.
1. Lack of Robust Authentication Mechanisms
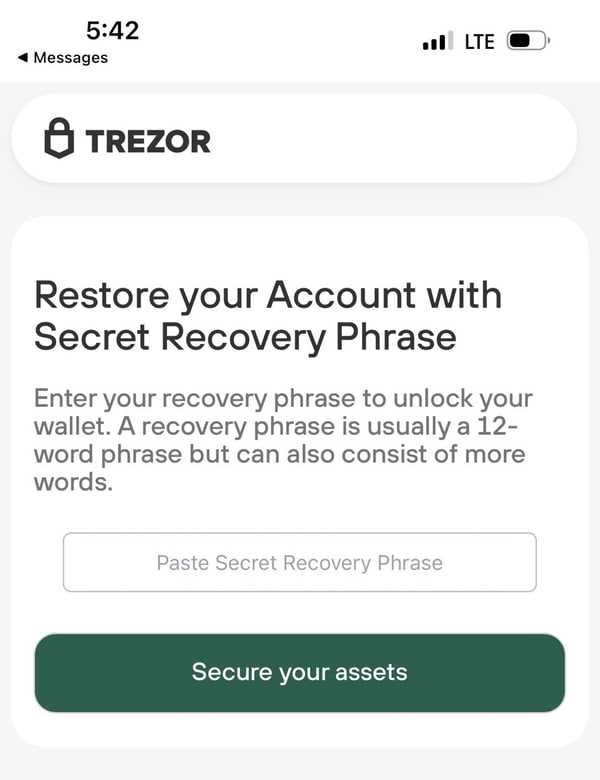
The breach highlighted the need for stronger authentication mechanisms in place. Trezor’s reliance on a single-factor authentication, namely a PIN code, proved to be inadequate. A multi-factor authentication system would have provided an extra layer of security against unauthorized access.
2. Insufficient Firmware Security Measures
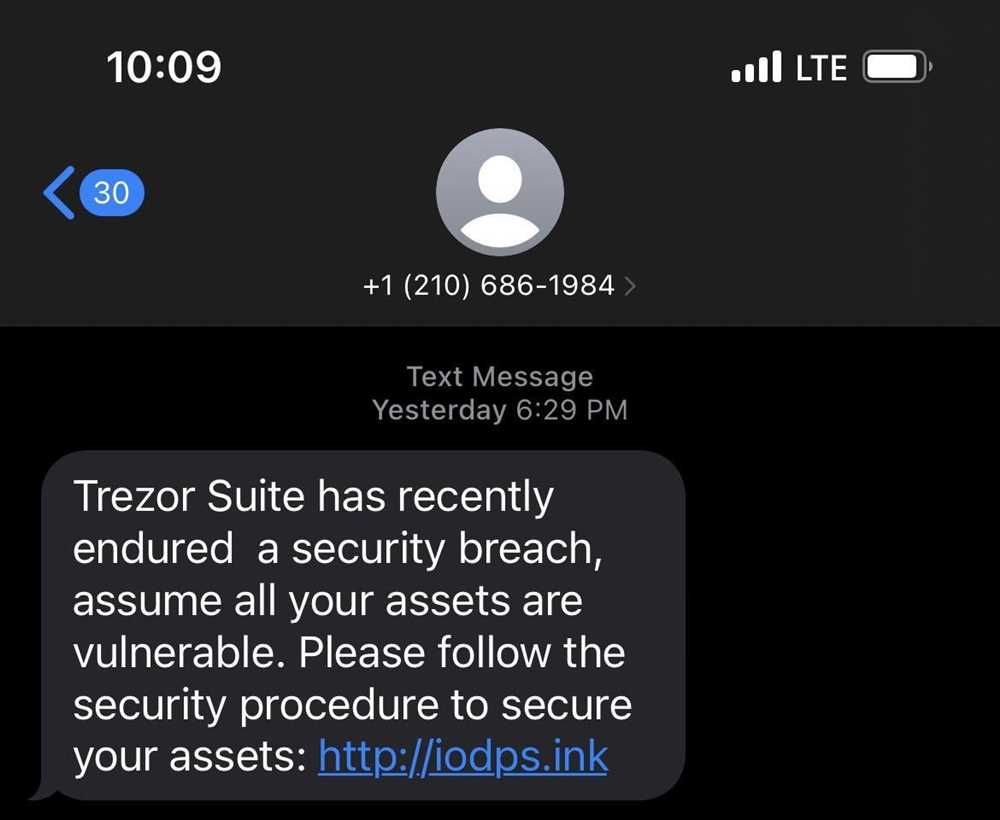
The firmware used in the Trezor device did not have sufficient security measures to protect against vulnerabilities. This allowed attackers to exploit weaknesses in the system, gaining unauthorized access to users’ funds. Regular firmware updates and a robust security testing process could have helped address these vulnerabilities.
- Inadequate Encryption: The lack of robust encryption in the firmware made it easier for attackers to bypass security measures.
- Lack of Secure Boot: A secure boot process would have ensured that only trusted firmware is loaded, preventing unauthorized modifications.
- Weak Password Protection: The device’s password protection mechanism was not strong enough, making it easier for attackers to guess or brute-force the password.
3. Lack of Penetration Testing
Regular and comprehensive penetration testing is crucial for identifying and addressing vulnerabilities. In the case of Trezor, a lack of such testing allowed security weaknesses to go undetected, increasing the likelihood of breaches.
4. Inadequate User Education
Many users of the Trezor device were not well-informed about the potential security risks and how to mitigate them. This lack of user education made it easier for attackers to exploit vulnerabilities through social engineering attacks, phishing attempts, or other manipulation techniques.
Overall, the Trezor breach exposed several security vulnerabilities that had significant implications. It underscores the importance of robust authentication mechanisms, firmware security measures, regular penetration testing, and user education in mitigating security risks.
In the Trezor Breach
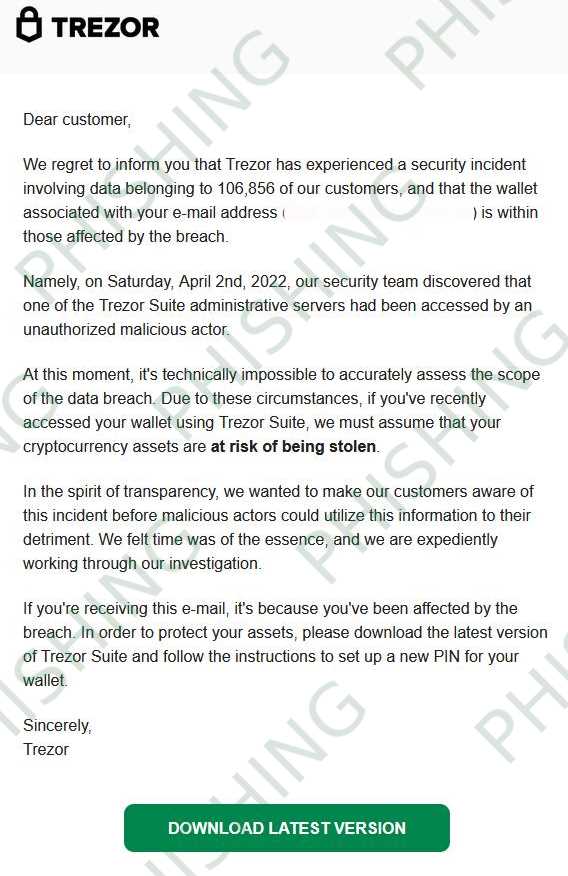
The Trezor breach is a significant event that exposed security vulnerabilities in the popular hardware wallet. This breach occurred when an attacker gained unauthorized access to the wallet’s private keys, compromising the security of the user’s cryptocurrency holdings. While the exact details of the breach are still being investigated, it is clear that there were weaknesses in the device’s security mechanisms.
One of the vulnerabilities found in the Trezor breach was related to the physical security of the device. The attacker was able to gain physical access to the wallet and extract the private keys by exploiting a flaw in the device’s design. This highlights the importance of physical security measures in protecting cryptocurrency assets, even in the case of hardware wallets.
Another vulnerability that was exploited in the Trezor breach was related to the device’s firmware. It is suspected that the attacker was able to install malicious firmware on the device, which allowed them to gain control over the private keys. This highlights the need for regular firmware updates and stringent security protocols to protect against such attacks.
In addition to these vulnerabilities, the Trezor breach also raised concerns about the overall security practices of the company. It is essential for hardware wallet manufacturers to prioritize security in their products and regularly test for vulnerabilities. In this case, it is clear that there were gaps in the security measures implemented by the company, which ultimately led to the breach.
As a result of the Trezor breach, many users have lost their cryptocurrency holdings, highlighting the risks associated with storing digital assets. It serves as a reminder for cryptocurrency holders to take proactive steps to enhance the security of their wallets and always remain vigilant against potential threats.
Lessons learned from the Trezor Breach
- Physical security measures are crucial for protecting hardware wallets.
- Regular firmware updates are essential for maintaining security.
- Hardware wallet manufacturers must prioritize security in their products.
- Users should take proactive steps to enhance wallet security.
- Constant vigilance against potential threats is necessary in the cryptocurrency space.
In conclusion, the Trezor breach has exposed vulnerabilities in the popular hardware wallet and serves as a reminder of the importance of robust security measures in protecting cryptocurrency assets. It highlights the need for both users and manufacturers to remain vigilant and proactive in ensuring the security of digital wallets.
Understanding the Impact
The recent breach of the Trezor wallet has raised serious concerns about the security of cryptocurrency storage. This incident has highlighted the vulnerability of hardware wallets and the potential risks associated with them.
Loss of Funds
One of the most immediate and significant impacts of the Trezor breach is the potential loss of funds for affected users. As hardware wallets are designed to securely store private keys offline, any compromise of these devices can result in the theft of cryptocurrency assets. In this case, users who relied on the affected Trezor wallet risk losing their entire investment.
Furthermore, the breach has exposed the fact that even well-established and widely-used hardware wallets are not impervious to attacks. This realization has raised concerns among cryptocurrency users about the overall security of their funds and has prompted a reevaluation of the methods used for storing and securing digital assets.
Compromised Information
In addition to the potential loss of funds, the Trezor breach has also resulted in the exposure of user data. This includes personal information such as email addresses and potentially even passwords.
While the immediate impact of this compromised information may not be as severe as the loss of funds, it still poses a significant risk to users. With access to user data, attackers could attempt to carry out phishing attacks or other forms of identity theft, potentially leading to further financial losses or unauthorized access to other accounts.
Moreover, the exposure of personal information raises concerns about privacy and data security, particularly in the context of the growing number of data breaches and cyber attacks.
Conclusion
The Trezor breach serves as a stark reminder of the importance of robust security measures in the world of cryptocurrencies. It highlights the need for constant vigilance and the adoption of best practices to ensure the safety of digital assets.
Furthermore, this incident underscores the need for both individuals and companies to remain proactive in managing their online security and safeguarding their sensitive information. The impact of the breach goes beyond the immediate financial loss, as it can have long-lasting effects on the trust and confidence of cryptocurrency users.
Disclaimer: The above text is for informational purposes only and should not be considered as financial or investment advice. Always do your own research before making any investment decisions.
Preventing Future Attacks
In light of the recent security breach involving Trezor, it is essential for future attacks to be prevented and for users to have confidence in the security of their digital assets. To achieve this, there are several steps that can be taken:
1. Regular Security Audits

Performing regular security audits is crucial to identify any vulnerabilities or weaknesses in the system. These audits should be conducted by experienced professionals who specialize in cybersecurity. By regularly assessing and addressing any potential security flaws, organizations can proactively protect against future attacks.
2. Continuous Employee Training
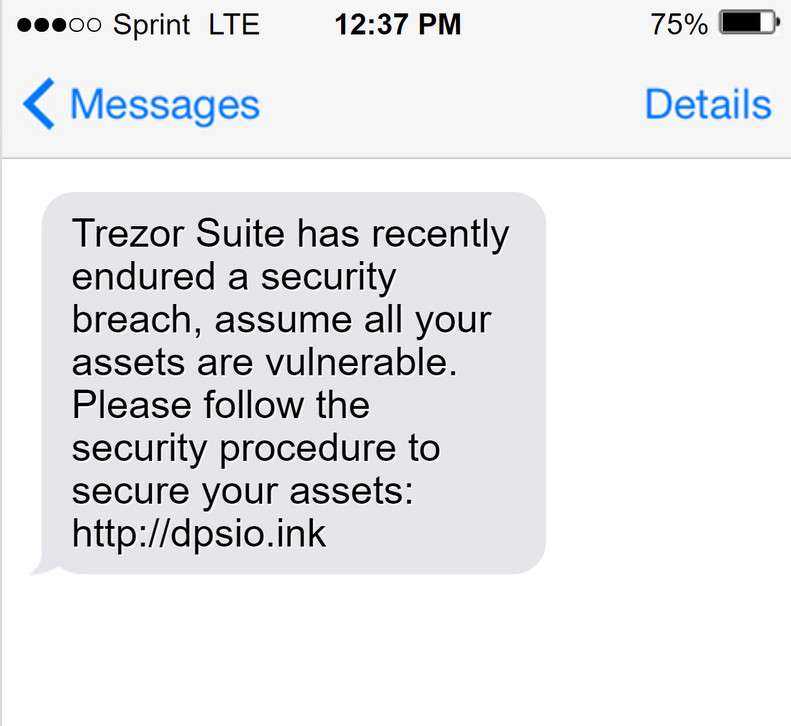
Employees should be provided with comprehensive cybersecurity training to educate them on best practices for handling sensitive information. This training should include topics such as password management, recognizing phishing attempts, and the importance of maintaining up-to-date software and security patches. Regular training sessions and assessments can help ensure that employees are always aware of the latest security protocols.
Furthermore, organizations should implement strict access controls to limit the number of employees with access to sensitive information. This reduces the potential attack surface and minimizes the risk of insider threats.
3. Multi-Factor Authentication (MFA)
 4. Timely Software Updates
4. Timely Software Updates
Keeping all software and firmware up to date is crucial in preventing attacks. Manufacturers should regularly release patches and updates to address any known vulnerabilities. Users should be alerted to these updates and strongly encouraged to install them as soon as possible. Promptly addressing vulnerabilities and ensuring that software is always up to date can significantly reduce the risk of successful attacks.
In conclusion, preventing future attacks requires a comprehensive approach that includes regular security audits, continuous employee training, the implementation of multi-factor authentication, and timely software updates. By prioritizing security and staying vigilant, organizations and users can better protect themselves against potential threats.
Q&A:
What is the Trezor Breach?
The Trezor Breach refers to a security vulnerability that was discovered in the Trezor hardware wallet. This vulnerability could potentially allow an attacker to gain unauthorized access to a user’s cryptocurrency funds.
How was the Trezor Breach discovered?
The Trezor Breach was discovered by a team of security researchers who were conducting an independent audit of the Trezor hardware wallet. During their investigation, they identified a vulnerability that could be exploited by an attacker.
What are the potential consequences of the Trezor Breach?
The potential consequences of the Trezor Breach are significant. If an attacker is able to exploit the vulnerability, they may be able to gain access to a user’s cryptocurrency funds, potentially resulting in financial loss.
Has the vulnerability in the Trezor hardware wallet been patched?
Yes, the vulnerability in the Trezor hardware wallet has been patched. The researchers who discovered the vulnerability reported it to the manufacturer, who released a firmware update that fixes the issue.
What can users do to protect themselves from the Trezor Breach?
To protect themselves from the Trezor Breach, users should ensure that they have updated their device’s firmware to the latest version. It is also recommended to use additional security measures, such as setting a strong PIN and enabling two-factor authentication.